
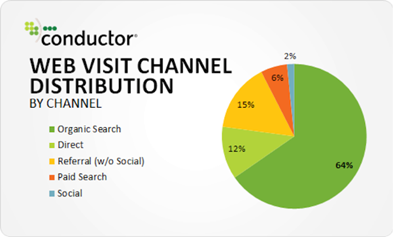
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is one of the most fundamental digital marketing strategies any business with an online presence should have. SEO is geared towards generating natural or organic traffic, which is basically the top source of traffic for most websites. This fact is established by many studies, including the recent study from Conductor where it highlighted that up to 64% of website traffic is generated from organic search.
On-page SEO is one of the most significant SEO/Ranking factors when it comes to search results. Doing good in these aspects can boost your overall SEO performance, and this is achieved by ensuring each of your important technical on-page SEO elements – which will be discussed in further detail in the following – are optimized to bring you top results.
The infographic (click to zoom):
1. Meta Title
According to inbound marketing expert Moz, the Meta Title tag is the single most-important element that would have the most significant impact on your on-page SEO. It is the clickable element in related search results that will direct your targeted audiences to your websites or landing pages. The metal title tells both search engines and search users in lengths below 55 characters how relevant your site is for a particular topic. This will create a big impact on search engine results rankings as well as the potential for generating clicks and visits from targeted audiences.
2. Meta Description
In 2009, Google made an announcement that Meta Descriptions do not really have a significant impact on search rankings from an algorithm perspective, but it is still very important to other aspects of your overall SEO efforts. Good meta descriptions will entice targeted visitors to click on your links and are thus important in increasing click through rates (CTR). Without an optimized meta description, search engines will simply pull text from your content – and these may not be the ones you want your targeted audiences to see first.
Even Google’s Matt Cutts agree that Meta Descriptions are important. Although he did mention that it is really not necessary to customize the meta descriptions on each of your pages, he recommended that you at least focus on optimizing pages with the highest ROI potential – those that will bring home the bacon.
3. Schema Mark-Up Tags
Search has evolved from traditional search algorithms to the new world of semantic search. This shift is brought about by the deeper need of matching high-quality relevant content with exactly what search users are really intending to look for.
In order for search engines to match your content with the intent and context of the search user, they need to “read” your content and confirm if they match. Since search engines cannot actually “read” content like humans do, they rely on microdata called schema mark-ups to interpret your web content. A standardized structured markup developed through the Schema project, a major collaborative project participated in by Bing, Google, Yahoo! and Yandex search engines.
Whether you’re trying to mark-up a video content in your website of the phone number entry in your Contact Us page, there is a corresponding schema that you can use as listed in the Schema.org site. With a proper schema integrated into your code, it would be easier for search engines to find your content and match it to search queries.
4. Open Graph Tags
The future of search is social and in the new age of Semantic Search, social relevance will weigh more in search results. To facilitate this, your website and its content should have the same functionality, or in more lay terms “speak the same language”, as social media networks. This will make your content and links more shareable in these networks, increasing engagement with targeted audiences which further leads to higher click-through rates and ultimately conversion.
To ensure this happens, you need to integrate Open Graph tags into your website pages’ code. First introduced by Facebook back in 2010, other social networks like Google+, Twitter and LinkedIn have adapted the system as the standard for displaying the links and content shared in these platforms. Facebook offers the Open Graph Object Debugger tool to let you check the right OG tags to use with your content. Examples of these Open Graph or OG tags include the following:
5. Twitter Cards
Twitter developed a system similar to Facebook’s Open Graph tags called Twitter Cards. These allow users to extend the information-giving capability of the 140-characters limitations of a tweet through a “View Summary” button just underneath the tweet. Just like the OG tags, Twitter cards can be included in the page codes like:
Like the Facebook OG Debugger, Twitter has the Card Validator that allows you to check your links before you share on social networks. Other tags are similar to the format used in Open Graph tags as shown in the following:
6. Sitemap
Just like what the name suggests, a sitemap provides a virtual map of your website that tells search engines all the links in your site. These can be done through static or dynamic HTML and XML site maps that directs search engines and users to a single page where all your page and section links are located. Plugins, modules, and extensions are available that can be used to generate a sitemap which you can submit to your search engine webmaster tools and have it re-indexed on a daily or a weekly basis.
7. H Tags
An H Tag or a Heading Tag is another on-page SEO element that helps search engines determine what your website content is all about so they can properly match it with search users’ queries. If you have large amount of content or post long articles longer than 1500 (which is better from a semantic search perspective) it would be best to have it subdivided into sections, with each section properly identify with a corresponding H Tag (or tags and so on)
Best Practices:
- There should only be one H1 tag for every web page. The H1 tag can also be your Main Title tag
- Embedding your main keywords strategically and naturally into your Header tags makes it more compelling for targeted audiences as well as search engine crawlers
- Header tags are different from style headers which are more focused on font formats and styles
8. Website Speed
Website loading speed is an important on-page SEO element that affects not only search ranking results but conversion rates as well. It affects the user experience, with faster loading sites naturally favored over slow ones. Factors that can increase website speed include:
- Compress images
- Host images separately
- Load less external objects
- Unconditional caching
- Compress and minimize code
9. Image ALT tags
Search engines really cannot “view” images just like humans can and would rely on Image ALT Tags to properly index images and return relevant ones during image search queries. These tags are not only used for letting search engine crawlers identify images but a highly descriptive tag embedded with relevant keywords.
10. Duplicate Content Check
One of the more important on-page SEO elements you should focus on is checking for duplicate content. Failure to do so may have some dire consequences if search engine crawlers find duplicate content. This is because it would be difficult for search engines to identify which particular content is the original or the best version. You can make use of Google’s Webmaster Tools and other third-party applications to check for duplicate content.
On-page SEO are as important as they once where since the principles and concepts of optimizing web pages for search were developed. However, other elements were introduced over the years as the Internet and social media channels continue to develop and evolve. Business owners and digital marketers need to evolve as well and learn all important aspects of these elements and their impact on this modern and new age of SEO.
Jomer B. Gregorio is a well-rounded expert when it comes digital marketing. Jomer is also known as a semantic SEO evangelist and practitioner. Check out our Digital Marketing Services today and let us help you in achieving positive and profitable results for your business.

